How to Build a Customer Segmentation Model: A Step-by-Step RFM Analysis Guide

Customer segmentation models like RFM can boost your ROI by up to 77% through targeted campaigns. Impressive, isn’t it?
RFM analysis creates a powerful customer segmentation model that works. The acronym RFM captures three key metrics – Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value – that reveal customer behavior patterns. These metrics tell us when customers last purchased, how often they buy, and the amount they spend.
You don’t need to be a Python or SQL expert to segment your customers effectively with RFM analysis. This approach helps you target your most valuable customers and create marketing strategies that resonate. Your customer satisfaction levels will improve as you focus your efforts where they matter most.
Let us guide you through building an RFM segmentation model from scratch. This practical approach gives you the tools to identify your high-value customers and spot potential fraud. You’ll learn to maximize your marketing budget with proven customer segmentation techniques using RFM analysis.
Understanding the RFM Segmentation Model
The RFM segmentation model has been around since the 1990s. Some credit Hughes for developing it in 1994, while others trace its origins to a 1995 article “Optimal Selection for Direct Mail” by Jan Roelf Bult and Tom Wansbeek.
What is RFM in customer segmentation?
RFM analysis is the life-blood of customer segmentation. It scrutinizes three key behavioral patterns instead of demographic traits. This approach groups customers by their actual buying habits and creates an actionable framework based on data. The model’s effectiveness comes from its simplicity – you already have all the required data in your customer database.
Businesses give scores from 1 to 5 for each RFM dimension, where higher scores show more valuable customers. These scores become the basis for targeted marketing campaigns that help companies decide which customers need investment, nurturing, or less attention.
Why recency, frequency, and monetary value matter
The RFM segmentation model’s components each give unique insights about customer behavior:
- Recency: Customers who bought something recently remember your brand better and tend to buy again. Their recent purchase shows they’re actively engaged and more likely to respond to future communications.
- Frequency: This measure reveals customer loyalty. Frequent purchases point to high satisfaction with your offerings, while sporadic buying might mean you need to re-engage these customers.
- Monetary Value: This metric carries the most weight in the analysis and assesses spending patterns. Some customers buy often but spend little, while others make big purchases less frequently.
These three metrics support the proven 80/20 rule – about 80% of revenue comes from the top 20% of customers.
How RFM is different from other segmentation models
RFM customer segmentation focuses on customer actions rather than static traits like age or location used in demographic segmentation. Psychographic segmentation looks at attitudes and values but relies on surveys and assumptions, making it less accurate.
RFM stands out because it’s easy to apply, measure, and act upon. The model uses transaction data you already have, so implementation needs minimal resources while still delivering valuable insights for customized marketing strategies.
Step-by-Step: Calculating RFM Scores
Building an RFM segmentation model needs a step-by-step approach to analyze customer behavior data. You’ll create a working customer segmentation framework that provides useful insights by following these three key steps.
Step 1: Collect and clean customer transaction data
The first step is to gather complete transaction data with purchase dates, customer identifiers, and monetary values. This data builds the foundation of your rfm analysis for customer segmentation. Your data quality check should include:
- Removing duplicates and fraudulent orders
- Correcting data entry errors and standardizing formats
- Handling missing values appropriately
- Aggregating transactions under unique customer IDs
Data preparation is vital – your customer segmentation model could lead to wrong marketing decisions without it. A clean dataset should show each customer’s latest purchase date (for recency), total purchases (for frequency), and total spending (for monetary value).
Step 2: Score recency, frequency, and monetary value
After preparing your data, give scores to each RFM dimension. Most companies use scales of 1-5, with 5 being the highest value. The scale you pick should match your customer base size:
- 1-3 scale for fewer than 30,000 customers
- 1-4 scale for 30,000-200,000 customers
- 1-5 scale for more than 200,000 customers
Sort customers into percentiles or quintiles for each dimension. Customers who bought items recently get higher recency scores. Those who haven’t bought anything in over a year might get a score of 1, while customers who purchased within three months get a 5.
Score frequency based on purchase count and monetary value based on total spending. Most businesses split customers into quintiles – top 20% get 5, next 20% get 4, and so on for each dimension.
Step 3: Combine scores into a single RFM score
The final step combines these three metrics into one complete RFM score. You can choose from several methods:
- Concatenation: Join the three scores together (e.g., R=4, F=3, M=5 becomes 435)
- Addition: Add up the three scores (e.g., 4+3+5=12)
- Weighted Average: Calculate based on each metric’s importance to your business
Some analysts use RFM = (R+F+M)/3 to get an average score between 1-5. Others multiply the scores (e.g., R×100 + F×10 + M) to see individual dimensions better.
These calculated scores become the foundation for creating meaningful customer segments that help target marketing strategies, whatever method you choose.
Segmenting Customers Using RFM Scores
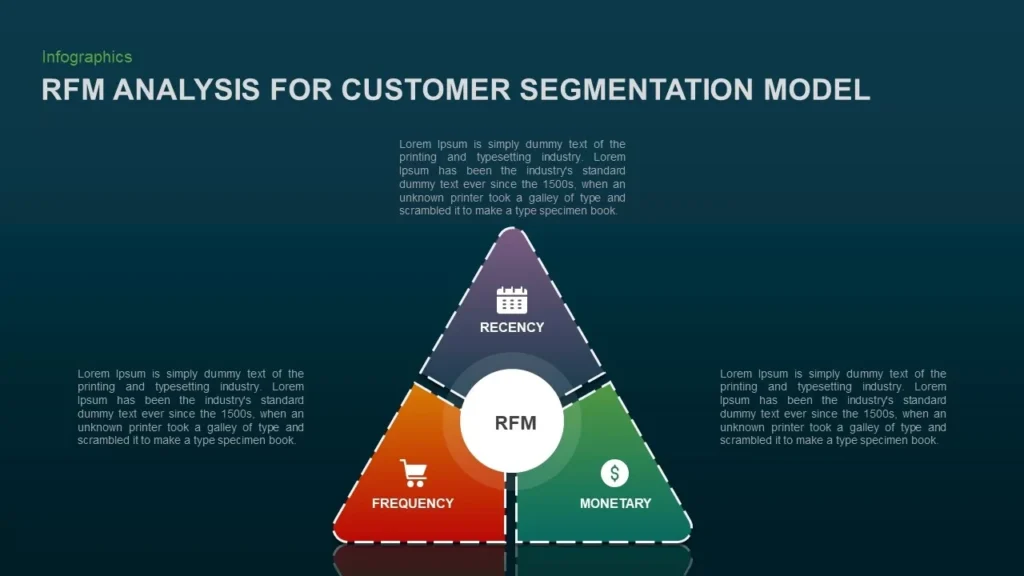
Image Source: SlideBazaar
The next significant step after calculating individual RFM scores transforms numerical values into meaningful customer segments. Raw data becomes strategic groups that help create targeted marketing initiatives.
Common RFM customer segments explained
RFM segmentation models identify several customer types based on their combined scores. The most valuable segments include:
- Champions (555, 554, 544): These customers make your best audience. They buy often, spend the most, and made purchases recently
- Loyal Customers (543, 444, 435): These valuable customers show strong engagement but spend less than Champions
- Potential Loyalists (553, 551): New customers show early signs of value and make perfect candidates to nurture
- At Risk (255, 254, 245): Regular customers whose purchases have declined make ideal targets for re-engagement campaigns
- Hibernating (111, 112, 121): These customers might be lost as they show lowest buying frequency and recency
How to group customers based on RFM scores
Two approaches define the grouping process. The concatenation method combines individual scores (e.g., R=5, F=4, M=3 becomes “543”). A 5-point scale creates up to 125 unique combinations. Many businesses prefer creating 10-11 strategic segments based on score patterns to reduce complexity.
Customer segmentation happens by identifying patterns across three scores. To name just one example, see customers with high recency (5) and frequency (4-5) but varying monetary scores – they form the “loyal customers” segment.
Visualizing segments with RFM grids or charts
RFM visualization makes complex customer data easy to understand. Popular visualization techniques include:
- RFM Grids: Two-dimensional representations plot recency against frequency, with color showing monetary value
- RFM Cubes: Three-dimensional visualizations use each axis to represent one RFM dimension
- Segment Size Charts: Bar or pie charts display customer proportion in each segment
These visual representations help teams identify segments that need immediate attention based on size and value.
Using RFM Segmentation in Marketing Strategy
The true value of RFM analysis emerges when you apply these insights to your marketing strategy.
Targeting high-value customers
Your “Champions” or “Soulmates” generate substantial revenue for your business. Targeted campaigns that use customer segmentation models like RFM can boost ROI by up to 77%. These high-value segments respond well to:
- VIP experiences, exclusive benefits, and early access to products
- Acquisition campaigns using lookalike audiences to find customers with similar profiles
- Loyalty programs that reward continuous purchases
Re-engaging at-risk or lost customers
Companies spend 5-25 times more to acquire new customers compared to keeping existing ones. You can reconnect with at-risk segments through:
- Automated win-back emails or push notifications that trigger when customers enter the “At Risk” category
- Ad campaigns that target recent browsers who haven’t made purchases
- Limited-time discounts or customized incentives based on past buying patterns
Personalizing campaigns based on segment behavior
Twilio’s research shows that customers spend 38% more when businesses customize their experience through proper segmentation. Smart personalization includes:
- Product recommendations that match customers’ monetary value scores
- Discount levels that align with each segment’s value
- Email templates with dynamic content based on RFM variables
Case study: RFM in fraud detection and loyalty programs
RFM analysis helps spot suspicious behavior patterns beyond marketing. A company found credit card fraud by identifying customers who made several large purchases quickly. Starbucks uses its customers’ data to customize rewards based on purchase history, which has substantially improved retention.
Conclusion
RFM analysis is a powerful tool that helps businesses understand customer behavior and improve marketing efficiency. Recency, frequency, and monetary value metrics work together to provide a detailed view of your customer base.
You don’t need complex technical skills to build a customer segmentation model with RFM analysis. The analytical insights help you identify valuable customers, find those likely to leave, and create targeted campaigns for each segment.
The practical nature of RFM segmentation makes it valuable. Your transaction records already contain all the data you need for simple implementation. Raw purchase data becomes applicable information that guides business decisions when you follow these steps.
The advantages go way beyond the reach and influence of simple customer understanding. Companies that run targeted campaigns based on RFM segmentation see ROI increases of up to 77%. Your marketing budget becomes more effective when you focus on the right customer segments at the right time.
Customer behavior evolves constantly. Regular updates to RFM scores will give your segmentation model relevance. Your RFM model guides marketing strategy by identifying champions who deserve VIP treatment and hibernating customers who need to reconnect.
Start with your existing transaction data today. Clean it, score it, segment it. Your customer relationships and revenue will grow through more customized, targeted marketing approaches.
Key Takeaways
Master RFM analysis to transform customer data into actionable segments that drive targeted marketing and boost ROI by up to 77%.
• RFM measures three key behaviors: Recency (how recently customers purchased), Frequency (how often they buy), and Monetary value (how much they spend) – creating data-driven customer segments.
• Follow the three-step process: Collect and clean transaction data, score each RFM dimension on a 1-5 scale, then combine scores to create comprehensive customer segments.
• Target high-value “Champions” differently: Offer exclusive benefits and VIP experiences to customers with high RFM scores while creating lookalike audiences for acquisition campaigns.
• Re-engage at-risk customers proactively: Use automated win-back campaigns and personalized incentives since retaining customers costs 5-25 times less than acquiring new ones.
• Personalize campaigns by segment: Customers spend 38% more when experiences are personalized through proper RFM segmentation, making targeted messaging essential for revenue growth.
The beauty of RFM lies in its simplicity – you already have all the transaction data needed to implement this powerful customer segmentation model and start seeing immediate improvements in marketing effectiveness.
FAQs
Q1. What is RFM analysis and how does it help in customer segmentation? RFM analysis is a data-driven technique that segments customers based on their Recency (last purchase date), Frequency (number of purchases), and Monetary value (total spend). It helps businesses identify valuable customer groups, personalize marketing strategies, and improve engagement and retention.
Q2. How do I create an RFM model for my business? To build an RFM model, start by collecting and cleaning customer transaction data. Then, score each customer on Recency, Frequency, and Monetary value (typically on a 1-5 scale). Finally, combine these scores to create comprehensive customer segments that can guide your marketing efforts.
Q3. What are some common customer segments in RFM analysis? Common RFM segments include Champions (high scores across all dimensions), Loyal Customers (consistent buyers), Potential Loyalists (recent customers with growth potential), At-Risk Customers (declining engagement), and Hibernating Customers (lowest recency and frequency).
Q4. How can I use RFM segmentation to improve my marketing strategy? Use RFM segmentation to tailor your marketing approach. Offer exclusive benefits to high-value customers, create re-engagement campaigns for at-risk segments, and personalize product recommendations based on customer behavior. This targeted approach can significantly increase ROI and customer satisfaction.
Q5. What’s the significance of the 80/20 rule in customer segmentation? The 80/20 rule in customer segmentation suggests that approximately 80% of your business revenue comes from about 20% of your customers. This principle underscores the importance of identifying and focusing on your most valuable customer segments to maximize business results.